Appendicitis: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Appendicitis is an affliction that can be painful and can potentially have serious consequences. The affected area is the appendix, a small, finger-like appendage of the large intestine, whose inflammation presents with slight, occasional pain and discomfort. Untreated appendicitis might lead to complications such as a ruptured appendix, extreme infections, and life-threatening consequences. Chase Lodge Hospital stresses that early identification of the potential symptoms of appendicitis and prompt intervention are essential.
This guide will describe all appendicitis-related aspects—causative agents, hallmark symptoms, UK diagnostic methods, and treatment.
What Causes Appendicitis?
Although the exact cause of appendicitis is often unclear, the most common reason is blockage in the appendix. Here are the following reasons:
- A hardened stool accumulation (faecalith).
- Swollen lymphoid tissue due to an infection.
- Intestinal parasites or tumours.
With this blockage present in the appendix, bacteria multiply within it, causing inflammation, swelling, and, consequently, rupture if untreated. Certain factors may increase susceptibility among individuals, such as having a relative with appendicitis or having undergone prior abdominal infections.
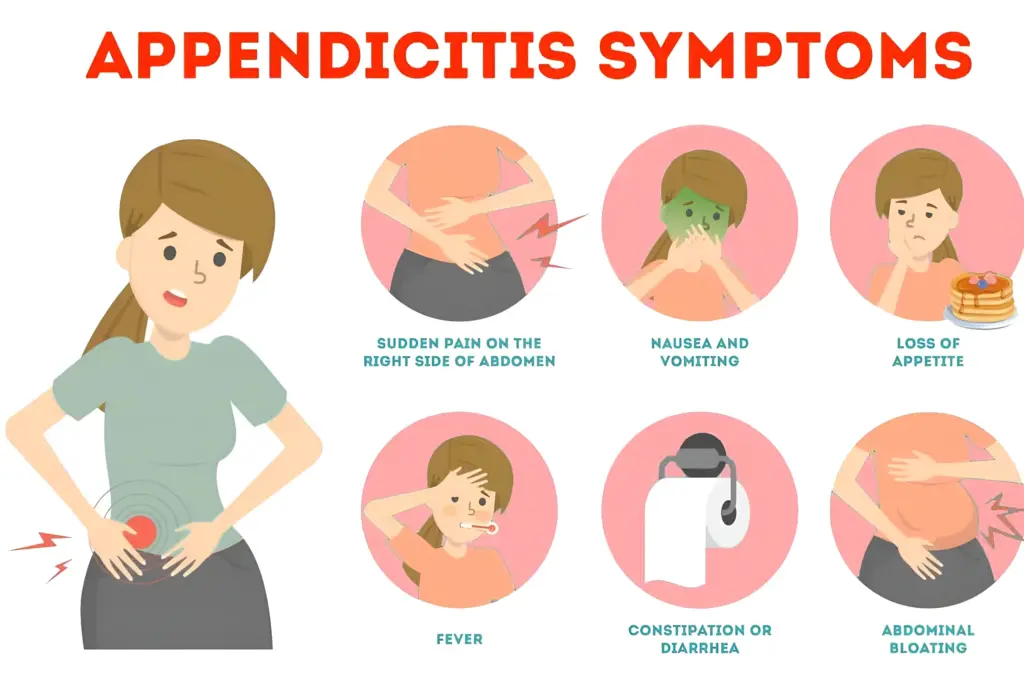
Key Symptoms of Appendicitis
Detecting the symptoms of appendicitis early may prevent further complications. The common symptoms include:
- Abdominal pain – The pain usually starts around the belly button, going down to the lower right side and increasing in intensity thereafter.
- Loss of appetite & nausea – A great number of patients feel nauseous, even vomiting.
- Fever & chills – A mild fever usually occurs when the condition worsens.
- Digestive issues – Some experience constipation or diarrhoea, along with bloating.
Symptoms may vary: children may present with more diffuse pain, while elderly individuals may have less severe presentations of symptoms that can delay diagnosis.
The 4 Stages of Appendicitis
Appendicitis progresses through four stages that describe the gradual progression of the disease:
- Early appendicitis – Mild inflammation with vague abdominal pain.
- Suppurative appendicitis – Increased swelling and infection, causing sharper pain.
- Gangrenous appendicitis – Death of the appendix due to impaired blood supply.
- Perforated (ruptured) appendix – The appendix ruptures, spilling infection into the abdomen (peritonitis).
A ruptured appendix is a surgical emergency requiring immediate operative intervention and antibiotics.
How is Appendicitis Diagnosed?
At Chase Lodge Hospital, doctors use many methods to confirm the diagnosis of appendicitis:
- Physical examination – Tenderness is checked during palpation of the abdomen.
- Blood tests – High white blood cell counts indicate infection.
- Imaging scans – With ultrasound (frequently used for children and pregnant women) or a CT scan, doctors can visualise the appendix clearly.
Since appendicitis symptoms may overlap with those of other conditions (such as urinary tract infections or ruptured ovarian cysts), proper testing is crucial.
Appendicitis Treatment Options
The usual treatment for appendicitis is an operation to remove the diseased appendix (appendectomy). At Chase Lodge Hospital, we perform:
- Laparoscopic (keyhole) surgery – Minimally invasive surgery using small incisions, resulting in quicker recovery.
- Open surgery – Reserved for extreme cases, such as a ruptured appendix.
If the appendix has ruptured, antibiotics are administered to patients pre-operatively for infection control. Recovery time for laparoscopic surgery is typically around 1–2 weeks, and open procedures may take longer.
Why Prompt Treatment is Crucial
Delaying medical care can lead to:
- Peritonitis – A dangerous infection of the abdominal lining.
- Abscess formation – Pockets of pus that may require drainage.
- Sepsis – A life-threatening response to infection.
If you experience appendicitis symptoms, seek emergency care immediately.
Conclusion:
Appendicitis is indeed a serious condition requiring immediate attention. Anyone familiar with the signs of appendicitis—abdominal pain that worsens, nausea, and fever—can take swift action. Our expert staff at Chase Lodge Hospital provide rapid diagnosis and effective treatment of appendicitis, including the most advanced surgical options.
If you suspect appendicitis, don’t waste a moment; call your GP or go directly to A&E. For further information or to book a consultation, visit Chase Lodge Hospital’s website or call our team of specialists.
References:
- NHS – Appendicitis
- Mayo Clinic – Appendicitis Symptoms & Causes